Itanagar, May 9 (IANS) A tribal body on Tuesday announced that no dialogue can be held with the Arunachal Pradesh and Central governments unless Chief Minister Pema Khandu clarifies that resolution of the Chakma-Hajong issue would be found within the state by fully complying with the 1996 Supreme Court judgment and granting of full rights to them as citizens of India. The Chakma Hajong Rights Alliance (CHRA), a representative organisation of the two tribal communities of Arunachal Pradesh, on Tuesday discussed Chief Minister's statement on March that he would call them to resolve the long standing issue and his statement on April 24 at a government function at Itanagar that the Chakma-Hajong problem would be resolved by distributing them in different states of India. "The Chakmas and Hajongs need resolution, not relocation. Under the laws of India, a person is considered as an ordinary resident after six months' residence but the state of Arunachal Pradesh has proposed relocation of the Chakmas almost 60 years after their settlement which is inhumane and cruel," CHRA Convenor Pritimoy Chakma said in a statement. The CHRA also adopted the resolution "to appeal to Khandu to not mislead the people of Arunachal Pradesh on the issue of the state being a tribal state and therefore protected, and the Chakmas and Hajongs cannot be permanently settled. Arunachal Pradesh is not recognised as a tribal state under the Constitution of India including Article 371(h) and the Chakmas and Hajongs were settled in the then North East Frontier Agency (NEFA) by the Government of India permanently", the statement said. It claimed that the Chakmas and Hajongs are not refugees, they are casting their votes and they are only victims of racial discrimination. The CHRA affirmed that dialogue can be held with the state and Central governments to find ways for implementation of the 1996 Supreme Court judgment and improvement of the deplorable economic conditions of the Chakmas and Hajongs as admitted by Chief Minister himself due to the exclusion from the development programmes of the state government. There are about 65,000 tribals belonging to Chakma and Hajong community in Arunachal Pradesh who fled from the then East Pakistan and were settled by the Central government in the then NEFA in 1964 to beef up security following the 1962 Indo-China war. Arunachal became a full-fledged State on February 20, 1987 and till 1972, it was known as the NEFA, administered by the Ministry of External Affairs with the Governor of Assam acting as representative to the President.
Arunachal's Chakma, Hajong tribals wants full rights as Indian citizens
- by Rinku
- May 09, 2023 2 minutes
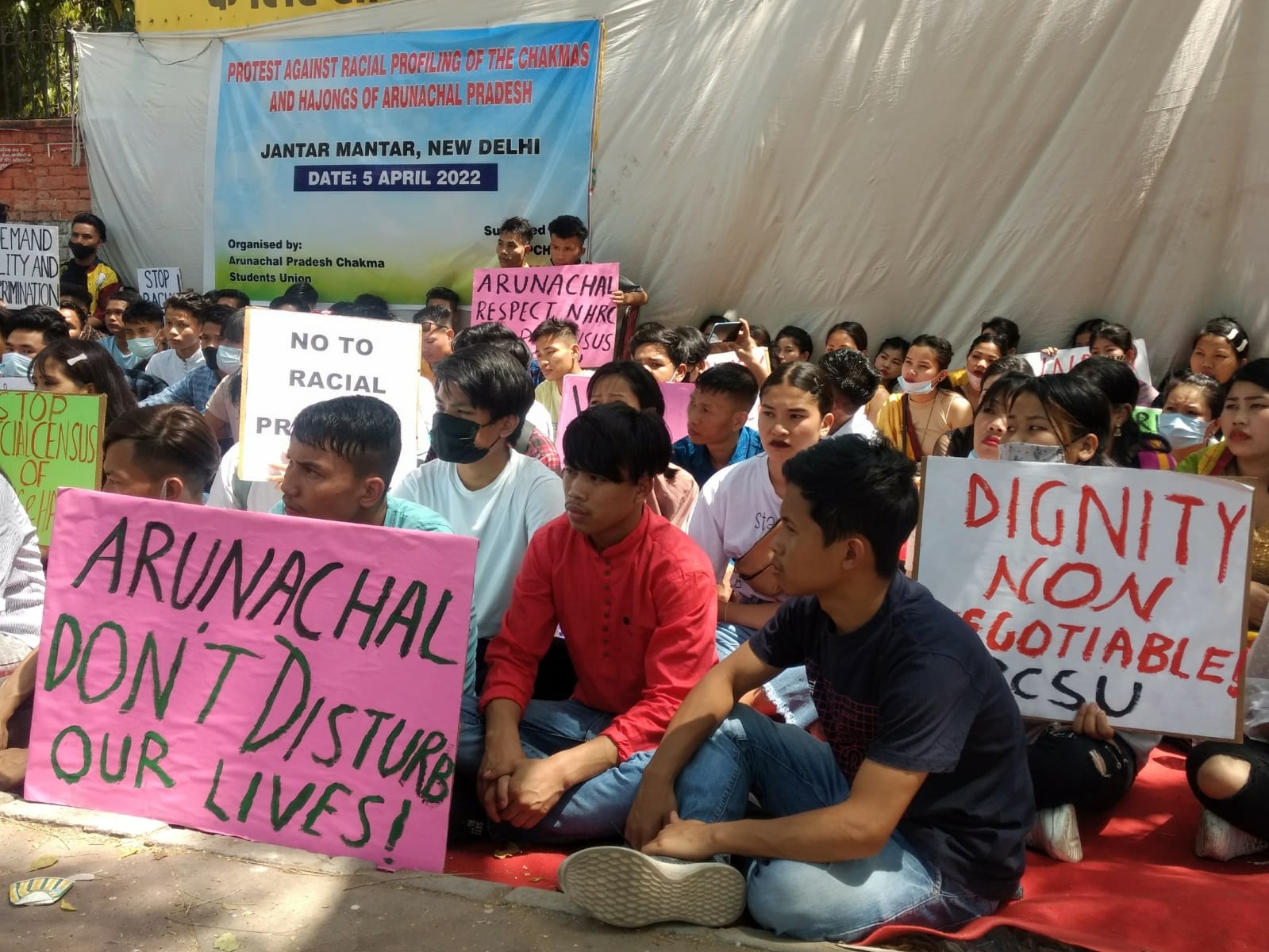

Chakma, Hajong tribals protests in Delhi against racial profiling in Arunachal. -- IANS